BLOGS
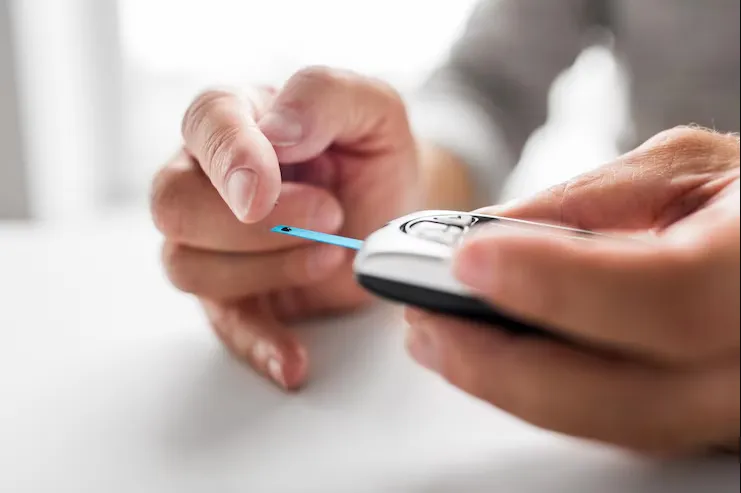

How does Diabetes Affect Women?
Diabetes affects a significant number of people worldwide and is a metabolic disorder that develops gradually due to elevated blood sugar levels. This condition has a profound impact on women's financial well-being. While both men and women are susceptible to diabetes, women are more likely to develop the disease because of specific physiological differences and risk factors. Understanding how diabetes uniquely impacts women is crucial for providing personalized care and improving outcomes. This comprehensive review will explore the physiological differences and risk factors that contribute to diabetes in women, as well as the specific ways diabetes affects their bone, mental, cardiovascular, and reproductive health. In the future, we'll look at powerful diabetes treatments and how to help women reach their goals of fantastic wealth and success despite type 2 diabetes insulin diabetes.
To know more about diabetes specialist arizona, side effects of diabetes in females, talk to experts at Gilbert Integrative Medical Center.
Physiological Differences and Risk Factors:
Diabetes can develop and progress in ways that significantly differ from men’s experiences, largely because women are more susceptible to specific physiological characteristics and risk factors. Hormonal fluctuations throughout a woman's life—during the menstrual cycle, menopause, and aging—can impact her ability to regulate glucose and maintain emotional stability. These hormonal changes can affect the body's response to varying blood sugar levels. Additionally, conditions such as gestational diabetes and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can increase a woman's risk of developing type 2 diabetes at any stage of her life.
Women, particularly those with certain characteristics such as a sedentary lifestyle, face unique challenges in managing diabetes. Women from African American, Hispanic, Asian American, or Native American backgrounds have higher rates of diabetes compared to Caucasian women. Furthermore, women with a history of gestational diabetes or those who have given birth to a child weighing more than nine pounds are at a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes earlier in life. To effectively manage women's diabetes aversion, position, and association, it is imperative to consider the physiological differences and danger elements discussed above.
To know more about symptoms of diabetes in women, talk to experts at Gilbert Integrative Medical Center.
Impact on Reproductive Health:
Diabetes can significantly impact a woman's quality of life, pregnancy outcomes, and fetal development, all crucial aspects of women's reproductive health. Poorly managed diabetes can lead to irregular menstrual cycles, disrupted ovulation, and increased risk of infertility in women. Moreover, diabetes heightens the risk of pregnancy-related complications such as gestational hypertension, preeclampsia, and macrosomia (high birth weight). Uncontrolled diabetes during pregnancy can also result in preterm labor, stillbirth, and long-term financial burdens for both mother and child. Maintaining healthy pregnancies and minimizing risks for both mother and baby requires diligent management, including consistent glucose monitoring and addressing other contributing factors. To lessen the possibility of adverse outcomes and to improve the health of both the mother and the unborn child, it is imperative to control and manage diabetes throughout pregnancy properly.
To get more information about the effect of excess sugar in females, consult with experts at Gilbert Integrative Medical Center.
Cardiovascular Health:
Cardiovascular disease is a leading cause of illness and death among patients with diabetes, with women being more susceptible to cardiovascular problems than men. Diabetes heightens the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and peripheral artery disease in women by disrupting fat metabolism, causing inflammation, and accelerating the development of arterial plaques. Women with diabetes often experience worse outcomes following cardiovascular events, highlighting the importance of early intervention and the strong link between risk factors and outcomes.
To improve cardiovascular health in women with diabetes, various lifestyle modifications are essential. These include regular exercise, weight loss, quitting smoking, and managing medications to control blood sugar, cholesterol, and blood pressure. To reduce the incidence of cardiovascular episodes and improve outcomes for women with diabetes, standard cardiovascular danger assessment and early management are crucial.
Mental Health:
Diabetes significantly impacts a woman's perceived overall life satisfaction, as well as her internal and external prosperity. It can be both enthralling and frustrating to subtly manage diabetes-related chores, such as monitoring glucose levels, accepting food guidelines, and administering medication. When people reflect on the difficulties of managing a chronic sickness, they can observe anxiety, fury, or perplexity. Hormonal imbalances that typically occur during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause may exacerbate personality changes and diabetes-related essentialness problems. Furthermore, women may associate diabetes with worries about potential side effects, such as problems with the eyes, kidneys, nerves, and cardiovascular systems. In addition to addressing the psychological impact of diabetes, supportive advantage providers should provide women with information, guidance, and support in coping with the challenging aspects of their condition.
Bone Health:
Diabetes increases a woman's risk of developing osteoporosis, a condition characterized by decreased bone mass and an increased risk of fractures. Several factors contribute to this heightened risk, including chronic inflammation, hormonal imbalances, and specific diabetes medications. Chronic inflammation can lead to weaker bones and a higher likelihood of fractures, disrupting bone structure and strength. Additionally, diabetes can significantly impair bone formation and bone remodeling. Some diabetes medications, such as thiazolidinediones and glucocorticoids, can further increase the risk of fractures and contribute to bone density loss. To encourage bone prosperity in women with diabetes, lifestyle modifications such as weight-bearing exercise, eatable calcium and vitamin D improvements, and quitting smoking are essential. Standard osteoporosis evaluation and break risk assessment are crucial for early detection and action.
Prevention and Management Strategies:
Diabetes-afflicted women need a comprehensive approach that addresses both changeable and immutable risk factors while managing their illness. Lifestyle modifications, such as routine physical activity, monitoring calories, maintaining a healthy weight, and quitting smoking, may help prevent or postpone the onset of type 2 diabetes in women. Diabetic patients should have plan evaluations for diabetes and associated illnesses, such as renal tainting, heart disease, and visual problems. Additionally, it is essential to achieve stable blood pressure, cholesterol, and glucose levels through medication association to reduce the risk of long-term complications and advance daily successful outcomes. Receiving support, practicing self-management, and utilizing healthcare services enable women to take leadership roles in their diabetes organizations and lead robust, fulfilling lives. By recognizing chance elements, encouraging robust lifestyle choices, and critical thinking, we are positioned to help women effectively manage their diabetes and advance toward average prosperity. We're prepared to work toward the day when all women with diabetes have access to the information, tools, and resources they need to thrive.
Conclusion:
Diabetes significantly impacts women's health, affecting various aspects of bone, mental, cardiovascular, and reproductive health. Due to a combination of distinct physiological differences and specific risk factors, women are more vulnerable to diabetes and its complications. Understanding these nuances and implementing effective management and intervention strategies are essential for reducing the burden of diabetes and improving outcomes for women. Through emphasizing chance components, encouraging robust lifestyle choices, and providing thorough information, we aim to empower women to take control of their diabetes and make every moment count. Together, we're prepared to work toward the day when all women—diabetes or not—have the resources and support they need to thrive. To know more about diabetes symptoms women, talk to our experts at Gilbert Integrative Medical Center.
Welcome to Gilbert Integrative Medical Center, your trusted source for comprehensive diabetes care in Arizona. Request an appointment online or by phone today.
Contact Us
Email: support@gilbertimc.com
Address:
2451 E Baseline Rd #100
Gilbert, AZ 85234
Phone Number:
Stay Connected:
Visit Us
Contact Us
Email: staff@wellness1stimc.com
Address:
2451 E Baseline Rd #100
Gilbert, AZ 85234
Phone Number:
Copyright 2024 . All rights reserved