BLOGS
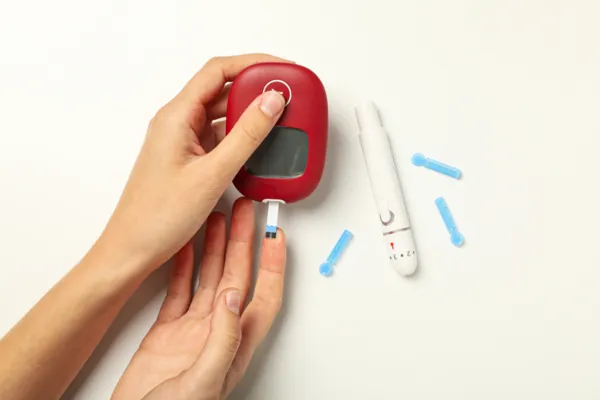

The Role of Sugar in Diabetes: Debunking Common Myths
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide. Managing diabetes involves maintaining a delicate balance in various aspects of your life, including your diet and sugar consumption. Sugar and its impact on diabetes have been a topic of confusion and misinformation. In this article, we'll debunk common myths surrounding sugar and diabetes, explore the role of sugar, provide guidance on intake and alternatives, and shed light on the connection between sugar and carbohydrates in diabetes.

Myth 1: Eating Sugar Causes Diabetes
One prevalent myth surrounding diabetes is the belief that consuming sugar directly leads to the development of the condition. However, this belief is not accurate. Diabetes is a complex health condition influenced by a combination of factors such as genetics, lifestyle choices, and environmental elements. While it's true that excessive sugar intake can contribute to weight gain and obesity, both of which are significant risk factors for type 2 diabetes, it's important to clarify that sugar alone is not the sole cause of diabetes.
Understanding the complexity of diabetes and its relationship with sugar is essential in dispelling myths and misconceptions. By debunking this particular myth, we can foster a more informed approach to diabetes management and promote a healthier lifestyle based on evidence and factual understanding. It's imperative to emphasize a holistic view of diabetes that considers various contributing factors, enabling individuals to make informed choices and effectively manage their health.
Read also: Treatments and Management For Your Diabetes
Myth 2: People with Diabetes Should Avoid Sugar Completely
Managing sugar intake is crucial for individuals with diabetes, but it's important to debunk the misconception that completely avoiding sugar is a necessity. Instead, the emphasis should be on managing the overall carbohydrate intake, which encompasses sugars, fiber, and starches. It's a comprehensive approach that involves being mindful of the types and quantities of carbohydrates consumed. This approach helps in understanding and controlling portion sizes, considering the glycemic index (GI) of foods, and ultimately leads to effective management of blood sugar levels.
The key to successful diabetes management is making informed dietary choices while understanding the impact of different carbohydrates on blood sugar levels. Not all carbohydrates are created equal, and they can affect the body differently. It's crucial to educate individuals about the glycemic index, which measures how quickly a particular food raises blood sugar levels. Foods with a low GI are broken down more slowly, causing a gradual rise in blood sugar levels, making them a better choice for individuals with diabetes. On the other hand, foods with a high GI can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar levels and should be consumed in moderation.
Incorporating these principles into a diabetes management plan allows for a more balanced and sustainable approach to sugar and carbohydrate intake. By focusing on the quality and quantity of carbohydrates and being conscious of portion sizes, individuals with diabetes can effectively regulate their blood sugar levels and maintain a healthy lifestyle. It's about making educated choices that consider the nutritional value of foods and their impact on overall well-being.
The Role of Sugar and Carbohydrates in Diabetes
Carbohydrates serve as the primary source of energy for the body, being broken down into glucose (sugar) during the digestion process. Glucose is then utilized by cells to fuel various bodily functions and activities. For individuals with diabetes, effectively managing carbohydrate intake is crucial due to the substantial impact that carbohydrates can have on blood sugar levels. By understanding the different types of carbohydrates and how they affect blood sugar, individuals can make informed choices, allowing for better management of diabetes and improved overall health.
Being mindful of the types of carbohydrates consumed is essential in diabetes management. Carbohydrates can be categorized into simple and complex forms. Simple carbohydrates, often found in sugars and processed foods, are quickly broken down by the body, causing rapid spikes in blood sugar levels. On the other hand, complex carbohydrates, present in foods like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, are broken down more slowly, leading to a gradual and steady increase in blood sugar levels. Understanding this difference empowers individuals to make appropriate dietary decisions, promoting stable blood sugar levels and ultimately enhancing their quality of life.
1. Simple Carbohydrates (Sugars): These are broken down quickly, causing rapid spikes in blood sugar levels. Common sources include table sugar, syrups, and the natural sugars found in fruits (fructose) and milk (lactose). Monitoring and moderating the intake of these sugars is vital for diabetes management.
2. Complex Carbohydrates: These are broken down more slowly, leading to a gradual rise in blood sugar levels. Complex carbohydrates are found in foods like whole grains, vegetables, and legumes. Including these in your diet can help in managing blood sugar levels effectively.
Tips for Managing Sugar Intake
1. Read Food Labels: Pay attention to the nutrition labels on packaged foods. Be aware of hidden sugars by looking for terms like sucrose, fructose, glucose, and high-fructose corn syrup.
2. Choose Whole Foods: Opt for whole, unprocessed foods like fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. These are lower in added sugars and provide essential nutrients.
3. Control Portion Sizes: Be mindful of portion sizes to manage your carbohydrate intake effectively. Use measuring cups and spoons to gauge serving sizes.
4. Monitor Blood Sugar Levels: Regularly check your blood sugar levels to understand how different foods, including sugars, affect your body.
Alternatives to Refined Sugar
For individuals with diabetes, choosing the right sugar alternatives can make a significant difference. Here are some alternatives to refined sugar that can be incorporated into a diabetes-friendly diet:
1. Stevia: A natural sweetener derived from the Stevia rebaudiana plant, stevia has no calories and does not affect blood sugar levels.
2. Erythritol: A sugar alcohol that occurs naturally in some fruits, it has minimal impact on blood sugar and is low in calories.
3. Xylitol: Another sugar alcohol found in fruits and vegetables, xylitol has a low glycemic index and does not cause rapid blood sugar spikes.
4. Monk Fruit Sweetener: Made from the monk fruit, it's a natural sweetener with no calories and does not affect blood sugar levels.
Final Thoughts
Understanding the role of sugar in diabetes is a fundamental aspect of effective diabetes management. Contrary to a prevalent myth, sugar alone is not the singular cause of diabetes. Diabetes is a multifaceted health condition influenced by a combination of genetic, lifestyle, and environmental factors. While excessive sugar consumption can contribute to weight gain and obesity, both of which are significant risk factors for type 2 diabetes, it is essential to clarify that sugar is not the sole culprit. To manage diabetes effectively, it's crucial to monitor and manage sugar intake in conjunction with carbohydrates, considering their impact on blood sugar levels.
Debunking common myths surrounding sugar and diabetes is imperative for fostering a more accurate understanding of the condition. Empowering individuals with diabetes to discern between myths and facts allows them to make informed dietary choices that positively impact their health. Additionally, incorporating sugar alternatives can be a valuable strategy in diabetes management. Consulting with healthcare professionals or registered dietitians can provide personalized guidance, aiding in the creation of dietary plans tailored to individual needs. This personalized approach offers a comprehensive strategy to manage sugar intake effectively, thus contributing to an improved overall state of health.
In conclusion, understanding the nuanced relationship between sugar and diabetes is pivotal in navigating the path of effective diabetes management. It's essential to dispel myths, embrace alternatives, and adopt a well-informed approach to sugar consumption. Seeking guidance from healthcare professionals ensures that dietary plans are personalized to individual needs, promoting better health outcomes for those living with diabetes. By promoting education and debunking myths, we can empower individuals with diabetes to lead healthier, more informed lives.
Welcome to Gilbert Integrative Medical Center, your trusted source for comprehensive diabetes care in Arizona. Request an appointment online or by phone today.
Contact Us
Email: support@gilbertimc.com
Address:
2451 E Baseline Rd #100
Gilbert, AZ 85234
Phone Number:
Stay Connected:
Visit Us
Contact Us
Email: staff@wellness1stimc.com
Address:
2451 E Baseline Rd #100
Gilbert, AZ 85234
Phone Number:
Copyright 2024 . All rights reserved